What is varicose veins?
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that are commonly found in the legs and feet. They occur when the valves in the veins that regulate blood flow towards the heart become weak or damaged, causing blood to pool and the veins to enlarge.
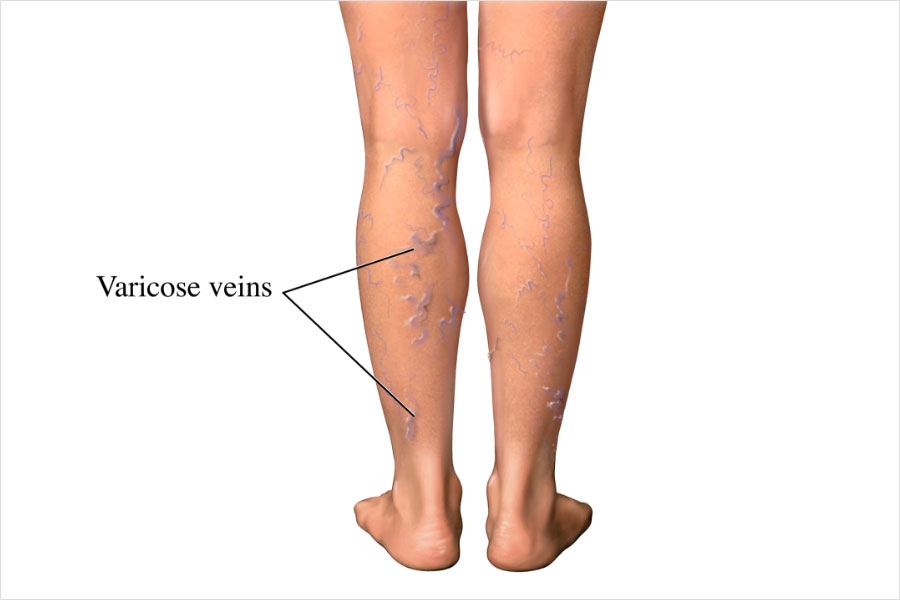
Appearance: Varicose veins are usually blue or dark purple and appear bulging or twisted, often looking like cords on the legs.
What are the symptoms of varicose veins?
- Aching or heavy feeling in the legs.
- Burning, throbbing, muscle cramping, and swelling in the lower legs.
- Worsened pain after sitting or standing for a long time.
- Itching around the veins.
- Skin discoloration around a varicose vein.
What are the causes of varicose veins?
- Age: Aging causes wear and tear on the valves in the veins.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop varicose veins, partly due to hormonal changes.
- Genetics: A family history of varicose veins increases risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts extra pressure on the veins.
- Standing or sitting for long periods: This reduces blood circulation.
What are the treatment options for varicose veins?
Treatment options for varicose veins include:
1. Lifestyle Modifications
- Exercise: Regular activity to improve blood circulation.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on veins.
- Elevation: Elevating legs to reduce swelling.
- Avoiding Long Periods of Standing or Sitting: Encouraging movement to prevent blood pooling.
2. Compression Therapy
- Compression Stockings: Graduated compression stockings help veins move blood more efficiently.
3. Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Sclerotherapy: A solution is injected into the vein, causing it to scar and close. Effective for smaller varicose veins and spider veins.
- Foam Sclerotherapy: Foam version of the sclerosant is used for larger veins, causing them to close.
- Endovenous Laser Ablation (EVLA): A laser fiber is inserted into the vein, emitting energy that causes the vein to collapse.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Uses radiofrequency energy to heat and close off the vein.
- Endovenous Chemical Ablation: Injection of a chemical solution to close off the vein.
4. Surgical Procedures
- Ambulatory Phlebectomy: Small incisions are made to remove superficial varicose veins.
- Ligation and Stripping: Tying off a vein before it joins a deep vein and removing it through small incisions. This is less common due to the advent of less invasive techniques.
5. Non-Thermal, Non-Tumescent Procedures
- VenaSeal (Medical Adhesive): A special adhesive is used to seal the vein.
- Clarivein: A catheter-based procedure that uses a rotating wire tip and a sclerosant to close the vein.
6. Transilluminated Powered Phlebectomy (TIPP)
- TIPP: A special light illuminates the vein from underneath the skin, allowing for precise removal with minimal incisions.
7. Laser and Light Treatments
- Surface Laser Treatments: For small spider veins, laser energy is applied to the skin to cause the veins to fade and disappear.
8. Venoactive Medications
- Flavonoids: Medications to strengthen vein walls and improve circulation.
How to prevent varicose veins?
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves blood circulation.
- Healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces pressure on the veins.
- Elevate legs: Raising your legs when resting helps reduce pressure on the veins.
- Avoid long periods of standing or sitting: Moving around helps keep blood flowing.
- Compression stockings: These can help improve circulation and alleviate symptoms.
