What is embolization?
Embolization is a minimally invasive procedure used to block blood flow to specific areas of the body, typically to treat abnormal bleeding, reduce blood supply to tumors, or manage other medical conditions.
Bronchial Artery Embolization (BAE)
Purpose
Bronchial Artery Embolization (BAE) is primarily used to treat severe or recurrent hemoptysis (coughing up blood), which can be caused by conditions such as:
- Chronic Infections: Tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, or fungal infections.
- Pulmonary Malignancies: Tumors in the lungs or airways.
- Congenital or Acquired Vascular Abnormalities: Such as arteriovenous malformations.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Chronic bronchitis or vasculitis.
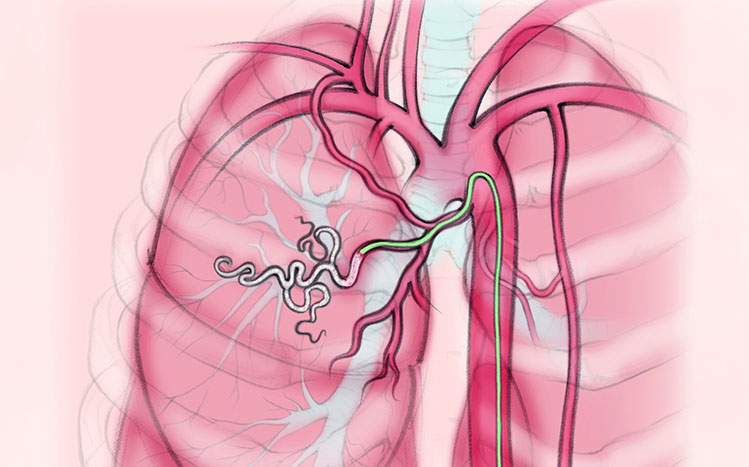
Benefits of bronchial artery embolization
- Immediate Control of Bleeding: Provides rapid cessation of hemoptysis.
- Minimally Invasive: Less risk and recovery time compared to open surgery.
- Repeatable: Can be performed multiple times if necessary.
Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE)
Purpose
Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) is primarily used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, which can cause:
- Urinary Symptoms: Frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, weak stream, and incomplete bladder emptying.
- Bladder Dysfunction: Chronic urinary retention or bladder stones.
- Quality of Life Impact: Significant discomfort and disruption of daily activities.
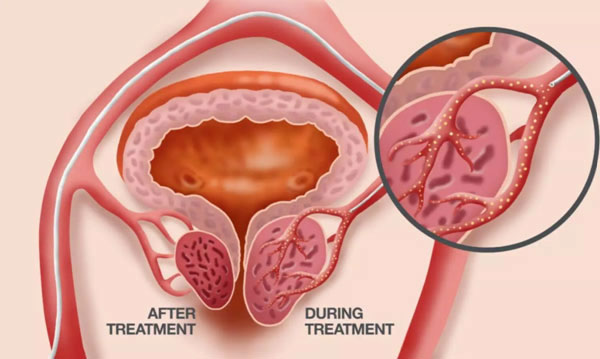
Benefits prostate artery embolization (PAE)
- Symptom Relief: Reduces urinary symptoms associated with BPH.
- Minimally Invasive: Lower risk and shorter recovery time compared to traditional surgical options (e.g., transurethral resection of the prostate, TURP).
- Preservation of Sexual Function: Lower risk of sexual dysfunction compared to surgical options.
Here are the other main types of embolization procedures
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
- Indication: Treatment of symptomatic uterine fibroids.
- Procedure: Tiny particles are injected into the uterine arteries to block blood flow to the fibroids, causing them to shrink.
- Benefits: Minimally invasive alternative to hysterectomy, preserves the uterus, shorter recovery time.
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE)
- Indication: Treatment of liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma).
- Procedure: Combines local delivery of chemotherapy with embolization to block the tumor's blood supply.
- Benefits: Targets the tumor directly, minimizing systemic side effects, effective in reducing tumor size.
Radioembolization (Y-90)
- Indication: Treatment of liver tumors, both primary and metastatic.
- Procedure: Radioactive microspheres (Yttrium-90) are injected into the hepatic artery to deliver targeted radiation therapy.
- Benefits: Combines embolization with radiation therapy, targets tumors while sparing healthy tissue.
Embolization for Gastrointestinal Bleeding
- Indication: Treatment of acute GI bleeding from ulcers, diverticulosis, or tumors.
- Procedure: Embolic agents are injected into the bleeding vessels to stop the hemorrhage.
- Benefits: Rapid control of bleeding, minimally invasive, avoids major surgery.
Varicocele Embolization
- Indication: Treatment of varicoceles (enlarged veins in the scrotum).
- Procedure: Embolic agents are injected into the affected veins to block blood flow, causing them to collapse.
- Benefits: Minimally invasive, quicker recovery compared to surgical ligation, effective in alleviating symptoms and improving fertility.
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome Embolization
- Indication: Treatment of pelvic congestion syndrome (PCS), characterized by chronic pelvic pain.
- Procedure: Embolic agents are injected into the pelvic veins to block blood flow to varicose veins, relieving pain.
- Benefits: Minimally invasive, effective in reducing pain and improving quality of life.
Peripheral Artery Embolization
- Indication: Treatment of arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), aneurysms, and other vascular anomalies.
- Procedure: Embolic agents are used to block abnormal vessels or aneurysms.
- Benefits: Minimally invasive, effective in preventing rupture or reducing symptoms.
Preoperative Tumor Embolization
- Indication: To reduce blood loss during surgical removal of highly vascular tumors.
- Procedure: Embolic agents are injected to block blood supply to the tumor, reducing its size and vascularity.
- Benefits: Decreases intraoperative bleeding, facilitates surgical resection.
Splenic Artery Embolization
- Indication: Treatment of splenic artery aneurysms or trauma-related splenic injury.
- Procedure: Embolic agents are injected into the splenic artery to reduce blood flow.
- Benefits: Minimally invasive, preserves spleen function, effective in controlling hemorrhage.
