What is genitourinary interventions?
Genitourinary interventions refer to a range of minimally invasive procedures designed to diagnose, treat, and manage conditions affecting the genitourinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra, and male reproductive organs.
Purpose of Genitourinary Interventions
- Diagnosis: To obtain tissue samples, detect abnormalities, and diagnose conditions such as tumors, infections, and obstructions.
- Treatment: To manage conditions like kidney stones, tumors, strictures, and urinary incontinence.
- Palliation: To relieve symptoms and improve quality of life in patients with advanced or incurable genitourinary diseases.
- Supportive Care: To provide drainage for obstructed urinary tracts or relieve pressure from fluid accumulations.
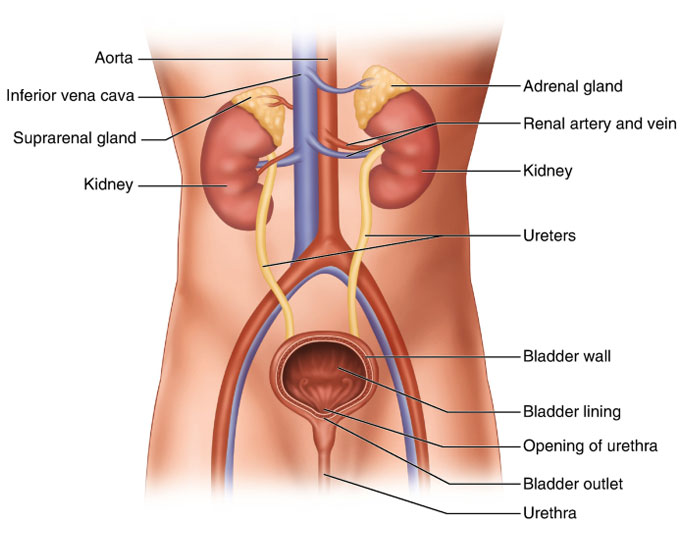
What are the common genitourinary interventions?
1. Percutaneous Nephrostomy
Percutaneous nephrostomy involves placing a catheter through the skin into the kidney to drain urine.
- Purpose: Used to relieve urinary obstructions caused by stones, tumors, or strictures; helps manage infections and hydronephrosis.
- Procedure: A needle is inserted through the skin into the kidney under imaging guidance, and a catheter is placed to drain urine externally.
2. Ureteral Stenting
Ureteral stenting involves placing a stent (tube) in the ureter to keep it open and allow urine to flow from the kidney to the bladder.
- Purpose: Used to treat or prevent ureteral obstructions caused by stones, tumors, or strictures.
- Procedure: A stent is placed using cystoscopy or retrograde pyelography under fluoroscopic guidance.
3. Renal Biopsy
Renal biopsy involves obtaining a small sample of kidney tissue for examination under a microscope.
- Purpose: Used to diagnose kidney diseases such as glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, and renal tumors.
- Procedure: A needle is inserted through the skin into the kidney under ultrasound or CT guidance to obtain a tissue sample.
4. Tumor Ablation
Tumor ablation techniques, such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and cryoablation, are used to destroy kidney tumors.
- Purpose: Provides a minimally invasive alternative to surgery for treating small kidney tumors.
- Procedure: A probe is inserted through the skin into the tumor under imaging guidance; heat (RFA) or cold (cryoablation) is used to destroy tumor cells.
5. Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE)
Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), an enlarged prostate gland.
- Purpose: Reduces urinary symptoms caused by BPH.
- Procedure: A catheter is inserted into the arteries supplying the prostate under imaging guidance, and embolic agents are injected to reduce blood flow to the prostate.
6. Bladder Botox Injections
Bladder Botox injections involve injecting botulinum toxin into the bladder muscle.
- Purpose: Used to treat overactive bladder and urinary incontinence.
- Procedure: Botox is injected into the bladder wall through a cystoscope.
7. Varicocele Embolization
Varicocele embolization treats varicoceles, which are enlarged veins in the scrotum.
- Purpose: Reduces pain and may improve fertility.
- Procedure: A catheter is inserted into the affected veins under imaging guidance, and embolic agents are injected to block the veins.
8. Lithotripsy
Lithotripsy uses shock waves to break up kidney stones into smaller pieces that can be passed in the urine.
- Purpose: Treats kidney and ureteral stones.
- Procedure: Shock waves are directed at the stones using an external device (extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy) or a probe inserted through the skin or ureter (intracorporeal lithotripsy).
What are the benefits of genitourinary interventions?
- Minimally Invasive: Reduced recovery time, less pain, and fewer complications compared to open surgery.
- Targeted Treatment: Directly addresses the affected area, providing effective management of symptoms and conditions.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: Allows for precise diagnosis through direct visualization and tissue sampling.
- Palliative Care: Helps manage symptoms and improve quality of life in patients with advanced genitourinary diseases.
- Supportive Care: Provides necessary interventions such as drainage and stenting to maintain organ function and relieve symptoms.
